
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire (322-185 BCE) was ancient India's first pan-Indian empire, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, reaching its zenith under Ashoka the Great.
Explore the great empires and ruling families that shaped the subcontinent

The Maurya Empire (322-185 BCE) was ancient India's first pan-Indian empire, founded by Chandragupta Maurya, reaching its zenith under Ashoka the Great.

Ancient Tamil dynasty that built a vast maritime empire, ruling Southern India from the 3rd century BCE to the 13th century CE with remarkable naval power.

Classical Indian empire (mid-3rd to mid-6th century CE) considered the Golden Age of India, spanning much of northern Indian subcontinent at its zenith.

The Pallava dynasty (275-897 CE) ruled southern India from Kanchipuram, creating architectural marvels and shaping Tamil and Sanskrit cultural traditions.

Classical Indian dynasty that ruled southern and central India from 543-753 CE, known for architectural innovations and patronage of arts
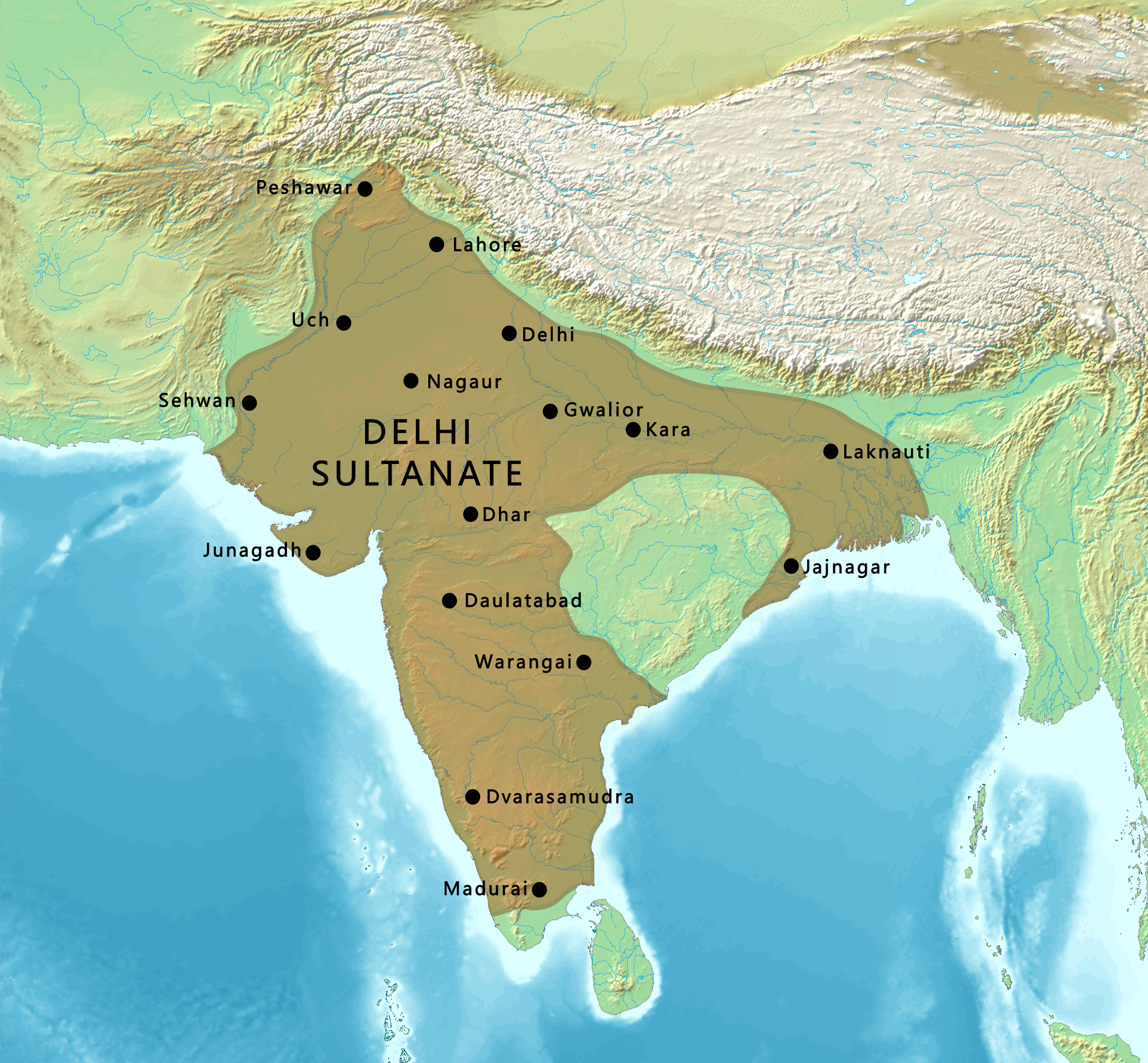
Late medieval Islamic empire (1206-1526 CE) that ruled much of the Indian subcontinent through five dynasties, introducing Indo-Islamic culture and architecture.
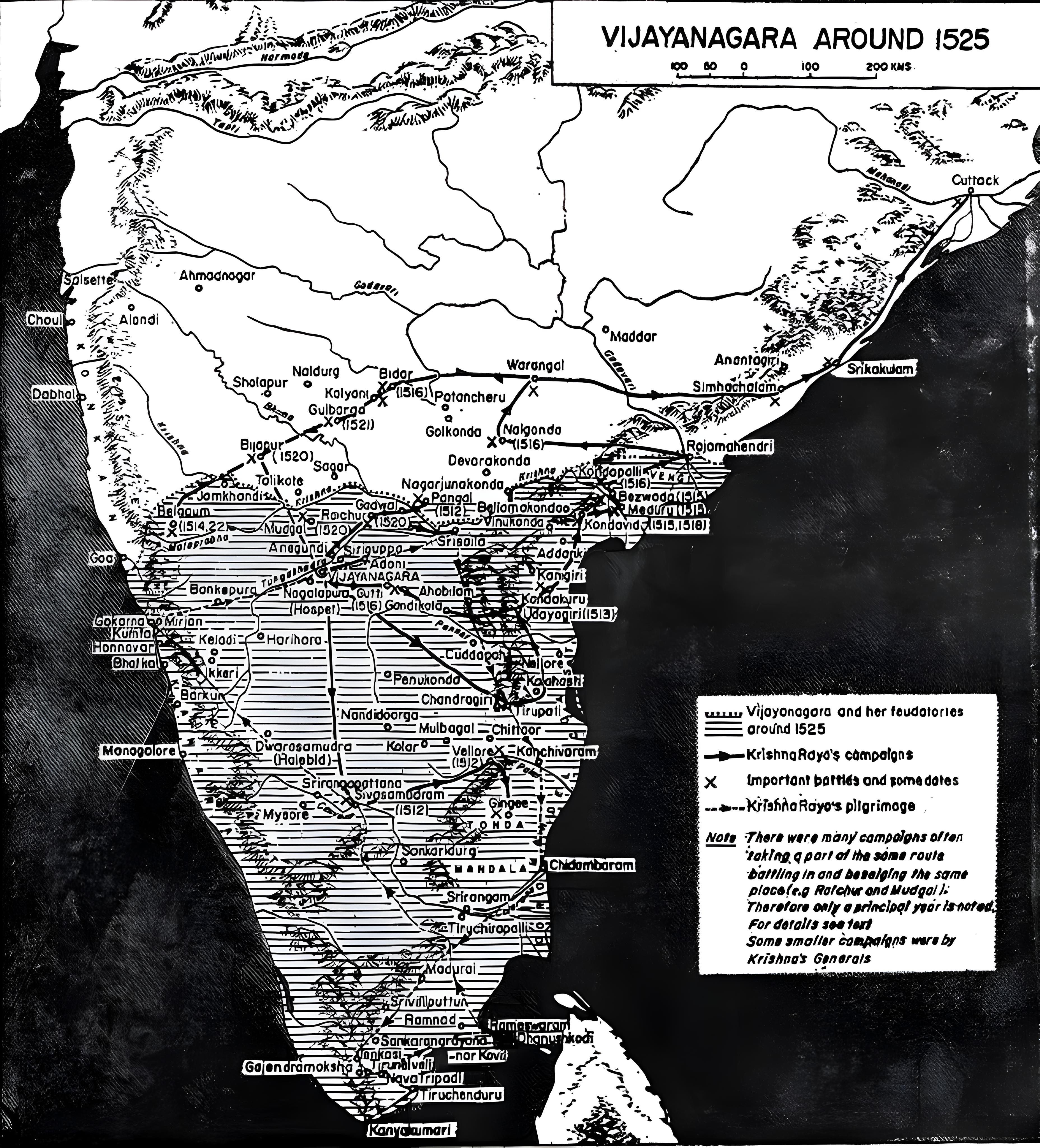
Late medieval Hindu empire (1336-1646) that ruled southern India, founded by Harihara I and Bukka Raya I, reaching its zenith under Krishna Deva Raya.
Early modern empire that ruled most of the Indian subcontinent from 1526 to 1857, known for its grand architecture, cultural synthesis, and administrative sophistication.

Early modern Indian empire (1674-1818) founded by Shivaji, which rose to dominate much of the subcontinent before falling to British colonial power.

Last major Indian power before British rule, the Sikh Empire (1799-1849) unified Punjab under Maharaja Ranjit Singh's secular governance.